Global Politics Update: Power Shifts, Conflicts & Democracy Under
Political landscapes around the world are in flux. New conflicts are emerging, democratic institutions are being tested, and global power dynamics are shifting rapidly. Here are some of the most significant political developments:
1.Gaza Conflict Escalation — Israel has launched a ground offensive in Gaza City, urging residents to evacuate amid intense hostilities. The humanitarian situation is worsening, with thousands displaced
2.Global Decline in Press Freedom — A report by the International IDEA finds that press freedom has seen a sharper fall in recent years than at any point in the last 50 years. Countries including Afghanistan, Myanmar and South Korea are among those with severe declines.
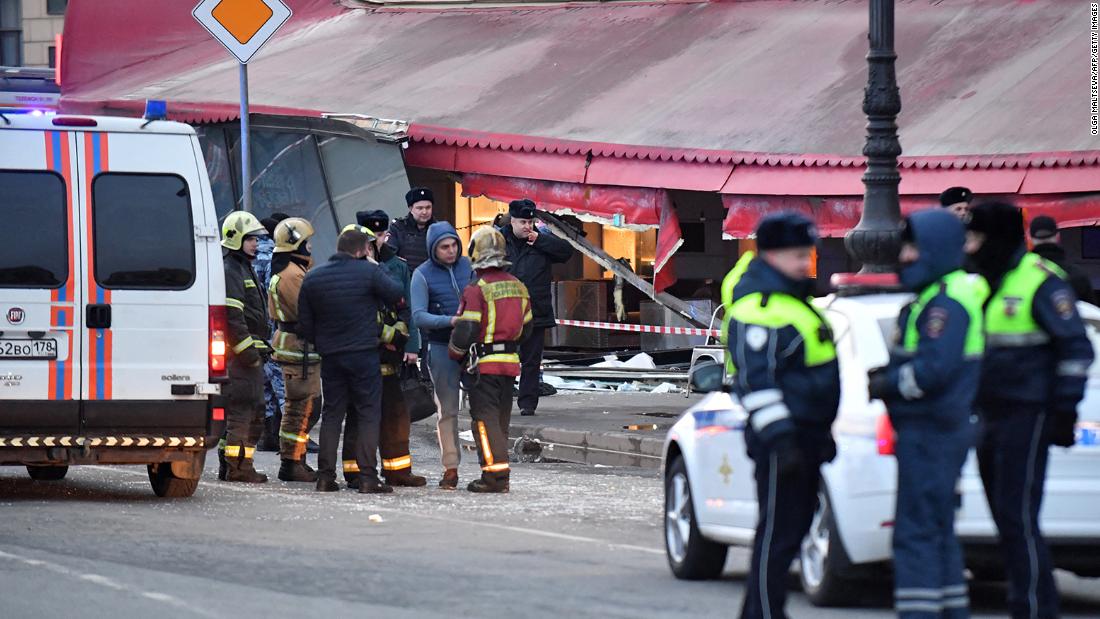
3.EU Sanctions & Regional Tensions — European leaders are calling for sanctions against Israel following airstrikes across the region, including Yemen. These acts have stirred diplomatic controversies and raised questions about regional stability
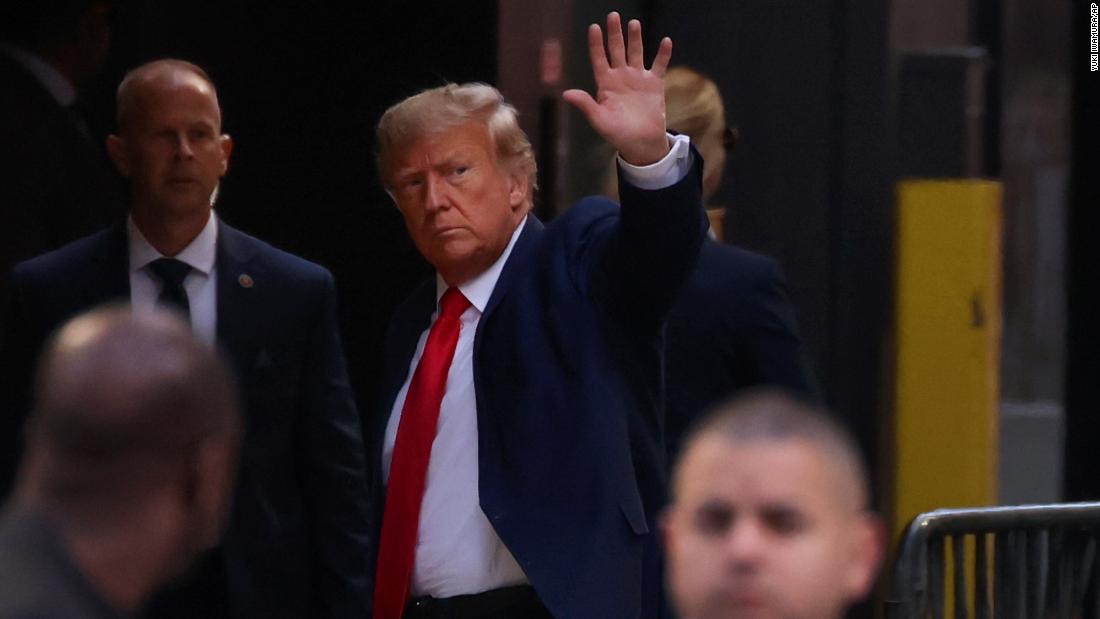
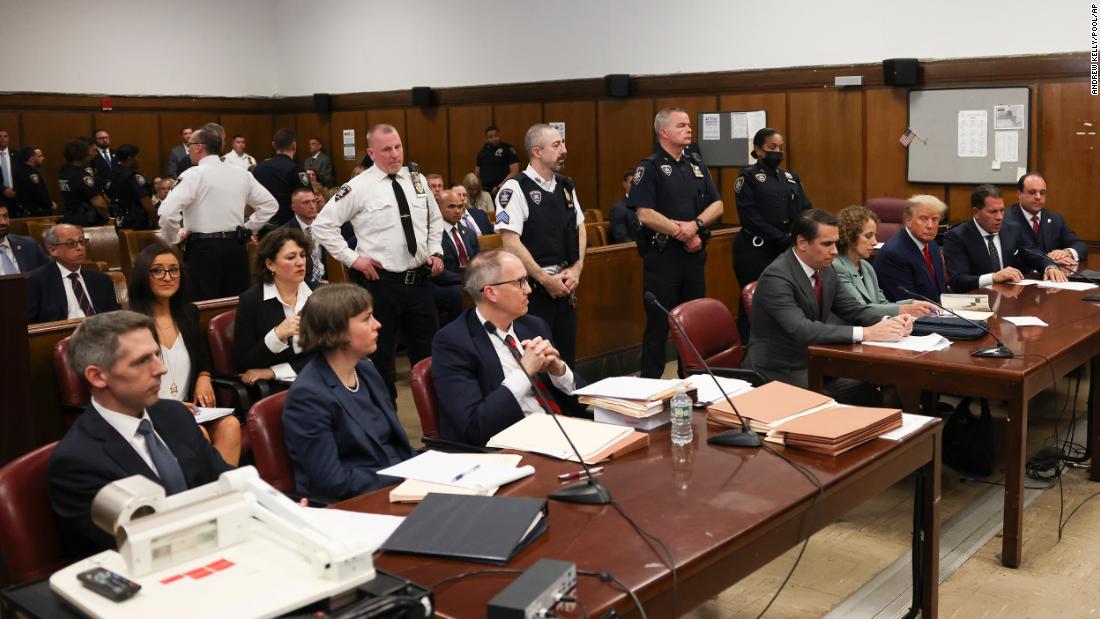
4.U.S. Domestic Politics & Polarization — In the U.S., political divisions remain deep. Controversies over civil rights, immigration, and institutional trust continue to fuel heated public debates. Observers worry this polarizing atmosphere may undermine democratic norms and governance effectiveness.
These events underscore a common theme: in many parts of the world, democracy, human rights, and freedom of expression are under pressure. Power is shifting — sometimes abruptly — and the world is watching closely to see how governments, international bodies, and citizens will respond.
Unlocking Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide to Studying in Hungary – Tuition Fees & Facilities for International Students
Study in Hungary: Details on Tuition, Facilities & Student Life (2025)
Hungary has become a popular destination for international students seeking quality higher education at relatively affordable costs. With reputable universities, many English-taught programs, extensive facilities, and a central European location, it presents strong value. In this article, we explore what you need to know about tuition fees, student facilities, and living costs when studying in Hungary in 2025.
1. Tuition Fees: What You Should Expect
Tuition fees in Hungary vary widely depending on several factors:
Program type (Bachelor’s, Master’s, PhD)
University (public vs. private)
Subject area (medicine, engineering, arts etc.)
Whether you are an EU vs non‑EU student
Here are some sample ranges:
Level / Field
Public Universities
Private / Specialized Institutions / Medicine & Dentistry
Bachelor’s (most programs)
≈ €1,500 – €6,000/year Study.eu+3Qogent Global+3Aspiredia+3
up to €8,000/year or more in private universities or competitive programs Study.eu+2Qogent Global+2
Master’s
≈ €2,000 – €8,000/year in public or mid‑range universities Aspiredia+2Qogent Global+2
higher for specialized, private or medical/dental fields, sometimes going over €12,000–€16,000/year a2z Edu Care+2Study.eu+2
Medicine / Dentistry / Veterinary
Typically among the highest; €8,000 – €20,000+/year depending on the institution and language of instruction Qogent Global+2Media Top Study World+2
Some examples of specific universities:
University of Pécs: Bachelor’s tuition around €5,500‑7,000, master’s around €6,000‑8,000. Career O'clock
University of Debrecen: Comparable ranges depending on subject. Career O'clock
Eötvös Loránd University (ELTE): More moderate fees in many programs, especially non‑medical. HunEducation+2Study.eu+2
Also keep in mind administrative fees: application fees (sometimes €150‑200), registration fees, occasionally deposits for housing etc. apply.budapestcollege.hu+1
2. Living Costs & Accommodation
Tuition is only part of the picture. Your total cost will include accommodation, food, transport, health insurance, books, and other living expenses. These differ significantly between cities (Budapest tends to be most expensive) and depending on your lifestyle.
Here’s a breakdown:
Accommodation:
University‑dormitories often cost €150‑€300/month, sometimes more depending on amenities. Scholars Avenue+2HunEducation+2
Shared apartments or rooms in furnished flats: €200‑€500/month depending on city and location. rpeducation.net+2Scholars Avenue+2
Private studio or one‑bedroom flats: can go higher in cost, especially in Budapest. HunEducation+2Aspiredia+2
Food, Transport, Miscellaneous:
Groceries: €100‑€250/month depending on how often you cook vs eat out. rpeducation.net+1
Public transport: €10‑€30/month for student passes in many cities. Scholars Avenue+1
Utilities & Internet: €50‑€120/month depending on housing type and location. Scholars Avenue
Health insurance: mandatory for non‑EU students; cost varies but can be €50‑€100/year or per month depending on coverage. rpeducation.net+1
Total Living Costs per Year:
In smaller university cities (e.g. Debrecen, Szeged, Pécs): €5,000‑€9,000/year including accommodation, food, transport etc. HunEducation+1
In Budapest: higher; could be €8,000‑€12,000/year depending on lifestyle. Qogent Global+1
3. Facilities & Academic Environment
One reason Hungary is attractive is the quality of facilities and student‐friendly infrastructure. Here are some of amenities and support systems you can expect:
Modern Campuses: Many universities have up‑to‑date lecture halls, labs, libraries, research centres, especially in disciplines like engineering, science, medicine.
Dormitories & Student Housing: On‑campus dormitories are common; some have shared rooms, basic furnishing, common areas. Private student residences also increasingly available with amenities like WiFi, laundry, communal kitchens. Hungary News In English+2mknccglobal.ac.uk+2
International Student Services: Offices to assist with visa, language support, counselling, orientation programmes. Many universities offer English‑taught courses.
Research Opportunities: PhD and master’s students often have opportunities for participating in research projects. Hungarian universities are involved in EU research funding and international cooperation.
Transport & City Life: Good public transport in most cities, with student discounts. Cultural life, museums, cafes, festivals available. Budapest especially rich in arts and history.
Health & Support Services: Health insurance schemes, clinics on campus or associated, student counselling, possibly mental health services.
4. Scholarships & Financial Aid
To help with the cost, there are several scholarship and financial aid options:
Stipendium Hungaricum: A popular government scholarship programme for international students which may cover tuition, accommodation, living costs.
University‑level scholarships: Merit‑based, need‑based, or subject‑based scholarships.
Some universities offer fee reductions, installment payments, or deferred payment in special cases.
Always check specific university websites for deadlines, eligibility, and whether scholarships cover just tuition, or also accommodation, travel, etc.
5. Tips for Budgeting & Planning
Choose city wisely: Cities outside Budapest tend to be cheaper. If your program is offered in Szeged, Debrecen or Pécs, life will be less expensive.
Start early for housing: Dorm rooms fill quickly. Private residences often more expensive.
Plan for non‑tuition costs: visa, insurance, books, materials, travel, leisure etc.
Language matters: English‑taught programmes are common, but some courses or requirements still expect knowledge of Hungarian; also day‑to‑day life sometimes easier with some Hungarian.
Check payment schedules: Whether tuition must be paid annually or per semester; whether you need to pay upfront before visa etc.
Conclusion
Studying in Hungary offers a strong value proposition: reasonable tuition (particularly in public institutions), good facilities, and a European environment without the extremely high costs seen in Western Europe or North America. However, as with any international study plan, costs can add up depending on choice of program, city, housing, and lifestyle. If you are considering Hungary, evaluate the exact university and program, factor in all living costs, explore scholarship options seriously, and budget carefully. For many students, Hungary can hit the sweet spot of quality + affordability + enriching student experience.
Study in Germany Without IELTS: A Complete Guide for International Students
Germany has become one of the most popular destinations for international students because of its world-class education system, tuition-free public universities, and excellent career opportunities. Many students, however, worry about English language requirements such as the IELTS exam. The good news is that it is possible to study in Germany without IELTS, as several universities and programs offer alternative options for proving language proficiency.
Why Germany?
Germany is known for its high-quality education, research facilities, and affordable tuition. Most public universities in Germany charge little to no tuition fees, making it a top choice for students around the world. Additionally, the cost of living is relatively lower compared to other European countries, and students are allowed to work part-time while studying.
How Can You Study Without IELTS?
Many German universities are flexible with their English-language requirements. If you can demonstrate that you can study in English through other evidence, you may not need an IELTS score. Here are the main pathways:
1. Medium of Instruction (MOI) Certificate
If you previously completed a degree or at least two consecutive years of education in English, you can request an official MOI certificate from your school, college, or university. This document states that English was the primary language of instruction for your coursework. Many German institutions accept this as proof of proficiency, especially for master’s programs.
2. Alternative English Tests
German universities often accept a variety of other standardized tests. Examples include:
TOEFL iBT (Internet-based Test) – widely recognized around the world.
PTE Academic – computer-based and quick to schedule.
Duolingo English Test – convenient online option with fast results.
Cambridge English Qualifications – such as C1 Advanced (CAE) or C2 Proficiency.
These tests might have different minimum scores than IELTS, so always check the specific requirement of each university and course.
3. University or Department Interviews
Some institutions conduct an online or in-person interview to gauge your speaking and comprehension skills. If you can hold a conversation and answer academic questions confidently, the university may waive the IELTS requirement.
4. Country-Based Exemptions
Applicants from countries where English is the official or native language—such as the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Australia, and New Zealand—are often exempt. Some universities also extend this to applicants from regions where English is the recognized medium of higher education.
Top Universities in Germany That Accept Students Without IELTS
Below are some respected universities known to consider applications without IELTS if other criteria are met:
University of Siegen – Public university offering multiple master’s programs in English. Students can use an MOI certificate or other recognized tests instead of IELTS.
Technical University of Kaiserslautern (RPTU Kaiserslautern-Landau) – Renowned for engineering and natural sciences. Many English-taught postgraduate programs accept alternative proofs.
Justus Liebig University Giessen – Known for life sciences and social sciences. Accepts medium of instruction certificates and other English exams.
University of Kiel (Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel) – Offers postgraduate programs that may waive IELTS if prior education was in English.
Free University of Berlin – Prestigious research university with several English-taught master’s degrees. MOI certificates and department interviews can substitute for IELTS.
RWTH Aachen University (selected programs) – In certain technical fields, alternative tests or an MOI certificate may be sufficient.
University of Freiburg (specific courses) – Some international master’s programs allow exemptions when other English-language evidence is strong.
Always verify with the admissions office of your chosen program, as policies differ between faculties and change over time.
Popular Courses to Study in Germany Without IELTS
Germany offers a vast selection of English-taught programs across disciplines. Particularly strong areas include:
Engineering: Mechanical, Electrical, Civil, Automotive, and Environmental Engineering are world-renowned.
Computer Science & IT: Artificial Intelligence, Data Science, Cybersecurity, and Software Engineering are in high demand.
Business Administration & Management: International Business, Finance, and Economics programs attract global students.
Natural Sciences: Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Environmental Sciences benefit from Germany’s strong research infrastructure.
Social Sciences & Humanities: International Relations, Political Science, and Cultural Studies provide diverse perspectives.
Health and Life Sciences: Biotechnology, Public Health, and Medical Engineering are growing fields.
Benefits of Studying Without IELTS in Germany
Choosing a program that doesn’t require IELTS offers several advantages:
1. Time and Cost Savings – Preparing for IELTS can be expensive and time-consuming. Skipping it frees resources for other parts of your application.
2. Flexible Entry Options – You can focus on your academic qualifications and professional achievements instead of standardized test scores.
3. Tuition-Free or Low-Cost Education – Many public universities charge little or no tuition fees for international students, keeping overall expenses manageable.
4. English-Taught Degrees – Hundreds of bachelor’s and master’s programs are offered entirely in English, allowing you to start immediately while you learn German gradually.
5. Work Opportunities – As a student, you can work part-time (up to 20 hours per week) and gain valuable professional experience.
6. High Employability – Germany’s strong economy and demand for skilled professionals make it easier to find work after graduation, whether you stay in Germany or move elsewhere in Europe.
7. Cultural and Language Growth – Living in Germany gives you the chance to pick up German naturally, which can boost your career prospects and personal development.
8. Final Thoughts
Studying in Germany without IELTS is definitely possible if you prepare the right documents and choose universities with flexible requirements. International students should check each university’s admission guidelines carefully and make sure they meet all other academic requirements. With tuition-free education, a strong job market, and numerous opportunities, Germany remains one of the best destinations for higher education.
"How to Make the Perfect Iskender Kebab"
İskender Kebab: A Taste of Turkish Tradition 🇹🇷
When it comes to iconic Turkish dishes, İskender Kebab stands out as one of the most beloved and flavorful meals. Originating from the city of Bursa, this dish has become a symbol of Turkish culinary heritage, enjoyed by both locals and food lovers around the world.
🛒 Ingredients
For the Meat
500 g lamb or beef (thinly sliced)
2 tbsp olive oil
2 tbsp yogurt
1 tsp garlic paste
Salt to taste
½ tsp black pepper
½ tsp paprika or chili powder
For the Tomato Sauce
1 cup tomato purée
2 tbsp butter
½ tsp salt
¼ tsp sugar
Other
3–4 pita breads or flatbreads
1 cup yogurt
2 tbsp melted butter
🍳 Preparation Steps
Marinate the Meat
In a bowl, mix the sliced meat with yogurt, olive oil, garlic, salt, black pepper, and paprika.
Let it marinate in the refrigerator for at least 2 hours (overnight is even better).
Prepare the Tomato Sauce
In a pan, melt the butter and add the tomato purée.
Season with salt and sugar, and cook on medium heat for 8–10 minutes until it thickens.
Cook the Meat
Heat a pan and cook the marinated meat until golden brown and tender.
Plating the İskender Kebab
Cut pita bread into pieces and place them on a serving plate.
Arrange the cooked meat on top.
Pour the tomato sauce generously over the meat.
Add a spoonful of yogurt on the side. Finally, drizzle hot melted butter over the dish for that signature İskender flavor.
✨ Serving Tips
Traditionally, İskender Kebab is served with grilled tomatoes and green peppers on the side.
A sprinkle of paprika on top makes the dish even more appealing.
İskender Kebab is more than just a meal—it’s a piece of Turkish history served on a plate. Its rich flavors, simple ingredients, and iconic presentation make it a timeless dish that continues to win hearts across the globe.
“Cybersecurity is one of the biggest challenges.Learn about the latest threats, solutions, and why protecting data is essential in today’s digital-first world.”
Introduction
The tech world is buzzing with excitement after a major breakthrough in quantum computing. Scientists have achieved a new milestone by developing a quantum processor that can solve complex problems far beyond the capability of classical computers. This innovation marks a turning point that could transform industries from healthcare and finance to cybersecurity and artificial intelligence.
What Happened?
Researchers at leading global tech companies and universities have successfully demonstrated a quantum chip with unprecedented stability and error correction. Unlike traditional computers that process information in bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use qubits, which can perform multiple calculations simultaneously. This advancement makes them millions of times faster for certain tasks.
Why It Matters
1.Medical Research – Quantum computers can analyze complex molecules, speeding up drug discovery and treatments.
2.Financial Systems – They can optimize investments, detect fraud, and improve global trading strategies.
3.Cybersecurity – Both a challenge and opportunity, as quantum computing may break old encryption but also create stronger security systems.
4.AI Development – Quantum power can significantly enhance machine learning models, making them smarter and faster.
Global Reactions
Tech Giants like Google, IBM, and Microsoft are racing to commercialize quantum computing for businesses.
Governments are investing billions to lead the global race, as quantum technology is seen as a national security priority.
Startups are emerging with creative applications, from climate modeling to logistics optimization.
Challenges Ahead
Cost – Quantum computers are still extremely expensive to build and maintain.
Stability – Keeping qubits stable (without losing information) is one of the hardest challenges.
Accessibility – It may take years before businesses and everyday people can fully access the benefits.
Final Thought
Quantum computing is still in its early stages, but 2025 has proven that the future is closer than we imagined. As researchers continue to push boundaries, quantum power could soon revolutionize how we live, work, and solve humanity’s biggest problems. The digital world is standing on the edge of a new era — and this breakthrough is just the beginning.